
The characteristics of seed plants
Seed Plants
All seed plants
have vascular tissue which is composed of xylem and phloem
use seeds to reproduce
have true leaves, true stems and true roots
do not need water for fertilization to occur( they can live away from water)
Seeds
Seeds are structures that contain an embryo ( a young plant) , a
cotyledon ( stored food), and a seed coat to protect the seed.

Seed
Dispersal
Seeds are dispersed or scattered in various ways:
Some animals eat fruits that contain seeds. Seeds first pass into the animal's digestive system then they are deposited in various areas.
Some seeds have structures that cling to the fur of animals for example burdock seeds have spiny hooks that attach to animal.
Seeds have structures that help them fly by wind like dandelion, milkweed and maple.
Some plants shoot seeds for example wisteria.
Germination
When a seed lands in a suitable environment, it sprouts or germinates. Seeds
need water, oxygen and a suitable temperature to germinate. The embryo
grows using the food stored in the cotyledons. The root tip emerges first and
anchors the seed to the ground. Root hairs begin to sprout from the soil. Then
the shoot, with its tiny leaves, sprouts from the soil. The tiny leaves turn
green and begin to manufacture sugars. When the stored energy in the cotyledons
is used, the seed falls off.

General characteristics:
Gymnosperms are the oldest types of plants.
They are plants whose seeds are naked (have no seed coats)
Seeds are found in cones:
- male cones are small and short-lived
- female cones are larger and contain seeds
Gymnosperms are four types:
Cycads
Ginkgo
Gnekophytes
Conifers or cone bearing plants (most common type) ex. pine trees, cedars and redwood.
Life Cycle
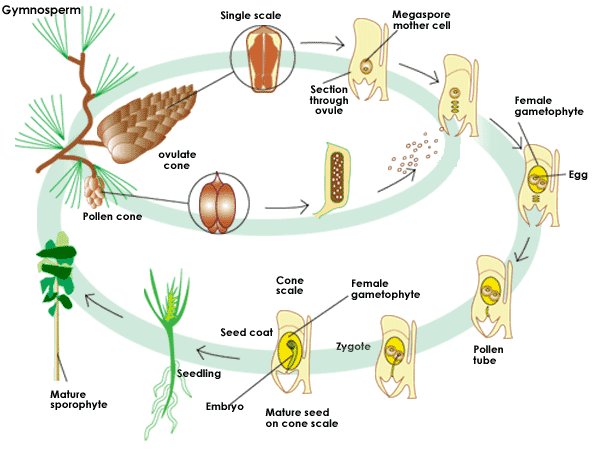
The female cone contains the egg.
The male cones produces the pollen grains that are dispersed by wind.
Pollination takes place when the pollen grains from the female structures
are transferred to the female cone.
Pollen grains produces a pollen tube to the egg. The sperm then travels in the
pollen tube. The sperm then joins the egg in a process called fertilization.
A zygote is then produced. The zygote develops to an embryo and
then to a seed.
Angiosperms
General characteristics
Most abundant plants . They are found in almost every environment on land e.g. dandelions, water lilies, cactuses, oak trees, lemons, maple trees, peaches, grapes, ect
Angiosperms produce seeds in fruits . Fruits protect and surround the seeds. Fruits help ensure the seeds survive as they are transported to areas where new plants can grow.
Angiosperms produce flowers that help plants reproduce Pollination in angiosperms depend on wind, on insects( bees, butterflies) and animals bats). Colorful flowers are usually pollinated by insects.


Types of Angiosperms
Angiosperms are two types: monocots and dicots. Each has certain characteristics .Study the pictures and find the characteristics of each.
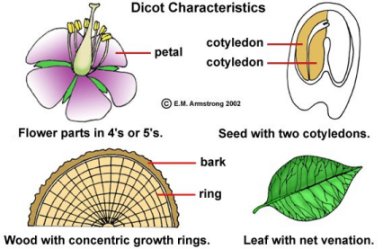
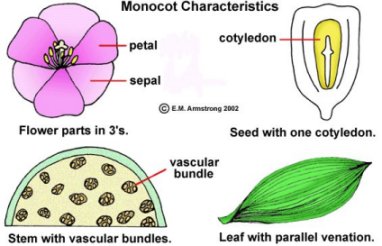
The following table summarizes the characteristics of monocots and dicots.
| Dicot | Monocot | |
| Two cotyledon | One cotyledon | Seed |
| Broad leaves with net-like veins | Narrow with parallel veins | Leaf |
| Tap root | Fibrous root | Root |
| Circular arrangement | Scattered | Vascular Tissue |
| Circular arrangement | Multiples of three | Flower parts |
| Roses cactuses, sunflowers, peanuts, peas | Grass, orchid, onions, lilies, palm | Example |
Flower structure
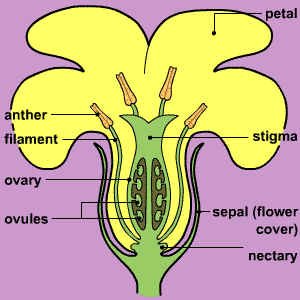
A flower helps angiosperms reproduce. It is made of several parts:
|
Location and function |
Name of flower part |
| Protective coverings on the outside of the flower – usually green | Sepals |
| Inside sepals and often colored to attract pollinating insects | Petals |
|
The male sex organs that produce
pollen (anther that produces the pollen` + supporting filament) |
Stamens |
|
The female sex organs that produce
ovules (ovary that contains the ovule + style + stigma that sticks the pollen) |
Pistil |
.
Cycle Life
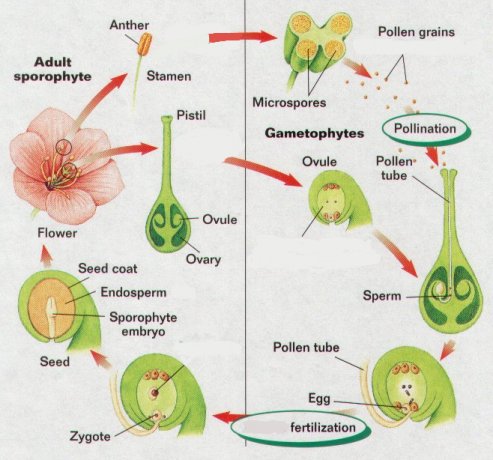
Stamen produces the pollen grains that are spread by air , insects and other
animals.
Pollen grains are transferred to pistil by a process called pollination.
If pollen grains land on stigma, a pollen tube forms. Sperm cells travel through
the tube. When a sperm fuses with an egg fertilization takes place The
fertilized egg develops to an embryo and then to a seed. The ovary then enlarges
and becomes a fruit. Then the other flower parts fall off.