| Plant Life Cycle | The Plant Kingdom |
| Mosses and Liverworts | Plant and Animal Cells |
| Ferns | Adaptation on Land |
Characteristics of all plants:
1. Plants are multicellular.

2. Plant cells are eukaryotes (cells with nuclei) with cell walls made of cellulose.
3. Plants don't move.
4. All plants are autotrophs. Photosynthesis it the process of making food. Look at the following illustration and answer the questions.
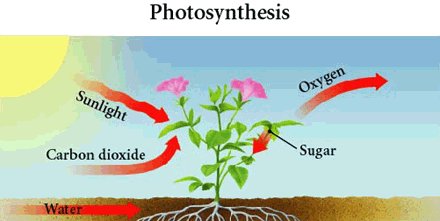
1. What are the raw materials of photosynthesis?
2. What are the products of photosynthesis?
3. What provides the energy for the chemical reaction of photosynthesis?
Check your answers.
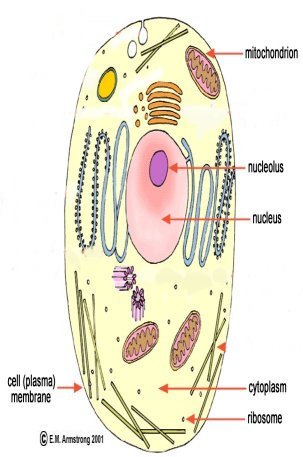
Compare the structure of a typical plant cell and a typical animal cell.
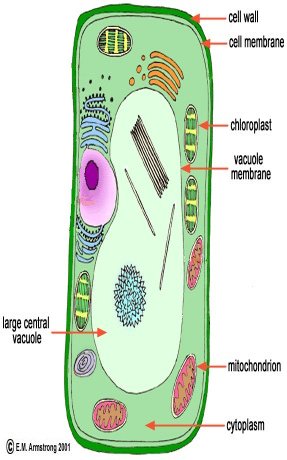
Plant cell
Animal cell
Animal and plant cells are alike in some
ways:
they both possess cell membranes, cytoplasm and a nucleus.
Cell membrane: the outer cell layer that controls what enters and what
leaves the cell.
Cytoplasm: is the gel-like substance inside the cell that makes up the
cell material.
Nucleus: stores the information needed for the cell's activities and
reproduction.
Now study the table below that summarizes the differences between plant and animal cells:
Plant cells
Animal cells
Have rigid cell walls
No cell walls
Have green chloroplasts
No chloroplasts
Thin lining of cytoplasm
Large cytoplasm
Vacuole filled with water
No vacuole
Cell walls: provides support and protection for
the cell. It is made of cellulose.
Vacuoles: store water, wastes and food materials.
Chloroplasts: green oval organelles that contain green compound called
chlorophyll. Chlorophyll traps energy from the sun to male sugars.
Remember that in every cell, all the different parts work together to meet the
needs of the cell.
For plants to survive on land they should :
1. Obtain water and other material: from their surroundings. Plants developed roots to absorb water and nutrients from soil.
2. Retain water. To reduce water loss, plants have developed waxy layer called cuticle.
3. Transport material. Large plants have developed a transport system called vascular tissue. Vascular tissue is made of xylem tat transports water and nutrients from roots to different parts of the plant. Phloem transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant.( stem, roots, flower)
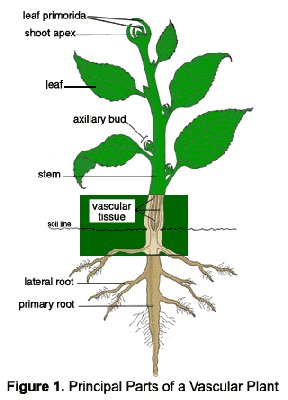
4. Support their bodies: vascular tissue supports the plant and exposes leaves to sunlight.
5. Reproduce: All plants undergo sexual reproduction that involves fertilization, which is the union of a sperm with an egg to produce a zygote.

All plants have two stages:
gametophyte stage which is the sexual stage. Male gametophyte produces sperms and the female gametophyte produces eggs.
sporophyte stage which is the asexual stage produces spores.
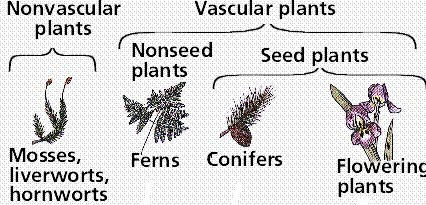
Characteristics of vascular and nonvascular plants:
Plants are two types : vascular and nonvascular
|
Vascular Plants |
Nonvascular Plants |
|
Have vascular tissue |
No vascular tissue |
|
Large in size |
Very small in size |
|
Live close or away from water |
Live close to water( absorb water directly) |
|
Have true stems, leaves and roots |
Have no true stems, leaves and roots |
|
Example: fern, gymnosperm and angiosperm |
Example: moss, liverwort and hornwort |
Characteristics of mosses
|
|
Life Cycle of Mosses
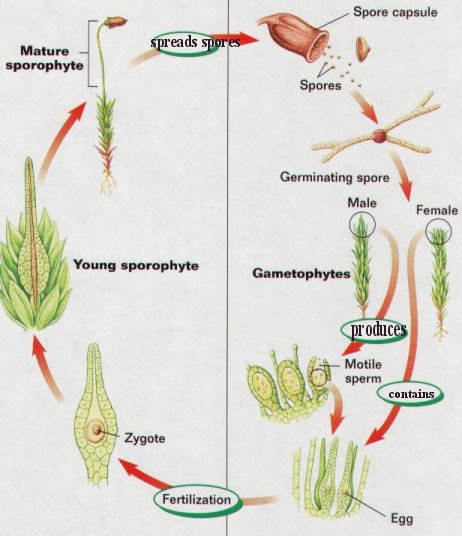
Mosses have tow stages in their life cycle: asexual
stage (the sporophyte) and a sexual stage ( the gametophyte).
The male gametophyte produces sperm and the female gametophyte produces the
eggs.
Sperms swim in water and fertilize the egg
on the female gametophyte.
A zygote results from fertilization.
A sporotphyte develops on the female gametophyte when the sporophyte matures,
the capsule on its top bursts and spores are spread by air. When spores land on
proper soil, they grow into a new gametophyte.
Hornworts and liverworts
|
Liverwort |
Liverworts: Look like human liver. They grow flat on moist rocks the stream. Hornworts: are found in moist soil, not on rocks. |
Vascular Plants are two types:
Seedless plants like ferns, clubmossses, and horsetails
Seed plants like pine trees, gymnosperms and angiosperms
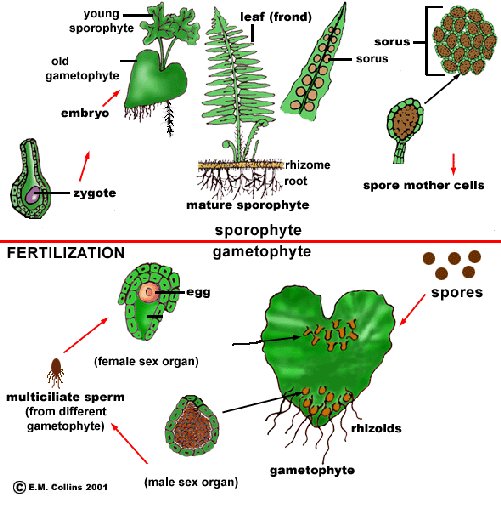
Ferns
Ferns are one of the oldest plants on earth. they grow
in dark, shady locations on rocks or in soil.
They have vascular tissue to transport water and food to different parts of the
plant and to support the plant.
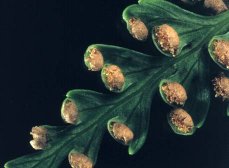
If we examine the fern frond, we realize small-circular spore bearing structures called sori. When the sori mature they split and release spores. Under favorable conditions, sores germinate and grow into a small heart shaped plant, gametophyte. The male gametophyte produce the sperms, and the female gametophyte produces eggs and following fertilization , the new fern plant is a sporophyte.
Life Cycle